- 一个小应用
一个小应用
当使用GtkApplication,main主函数非常简单。我们仅仅调用了g_application_run() 并给出一个应用范例。
#include <gtk/gtk.h>#include <exampleapp.h>intmain (int argc, char *argv[]){return g_application_run (G_APPLICATION (example_app_new ()), argc, argv);}
所有的应用程序逻辑都在GtkApplicaton的子类中。我们的范例还没有任何有趣的功能。它所做的只是当它没有传递参数而被激活时打开一个窗口,在传递了参数被激活时打开给定的文件。
为了处理这两种情况,我们重载了activate()vfunc,当应用程序被加载没有命令行参数时它被调用,当应用程序被加载并带有命令行参数时,调用open()vfunc。
想知道更多关于GApplication入口知识,请查看GIO文档。
#include <gtk/gtk.h>#include "exampleapp.h"#include "exampleappwin.h"struct _ExampleApp{GtkApplication parent;};struct _ExampleAppClass{GtkApplicationClass parent_class;};G_DEFINE_TYPE(ExampleApp, example_app, GTK_TYPE_APPLICATION);static voidexample_app_init (ExampleApp *app){}static voidexample_app_activate (GApplication *app){ExampleAppWindow *win;win = example_app_window_new (EXAMPLE_APP (app));gtk_window_present (GTK_WINDOW (win));}static voidexample_app_open (GApplication *app,GFile **files,gint n_files,const gchar *hint){GList *windows;ExampleAppWindow *win;int i;windows = gtk_application_get_windows (GTK_APPLICATION (app));if (windows)win = EXAMPLE_APP_WINDOW (windows->data);elsewin = example_app_window_new (EXAMPLE_APP (app));for (i = 0; i < n_files; i++)example_app_window_open (win, files[i]);gtk_window_present (GTK_WINDOW (win));}static voidexample_app_class_init (ExampleAppClass *class){G_APPLICATION_CLASS (class)->activate = example_app_activate;G_APPLICATION_CLASS (class)->open = example_app_open;}ExampleApp *example_app_new (void){return g_object_new (EXAMPLE_APP_TYPE,"application-id", "org.gtk.exampleapp","flags", G_APPLICATION_HANDLES_OPEN,NULL);}
应用程序中另一个受GTK+支持的重要的类是GtkApplicationWindow。它通常也是子类。我们的子类不做任何事,因此我们只得到一个空的窗口。
#include "exampleapp.h"#include "exampleappwin.h"#include <gtk/gtk.h>struct _ExampleAppWindow{GtkApplicationWindow parent;};struct _ExampleAppWindowClass{GtkApplicationWindowClass parent_class;};G_DEFINE_TYPE(ExampleAppWindow, example_app_window, GTK_TYPE_APPLICATION_WINDOW);static voidexample_app_window_init (ExampleAppWindow *app){}static voidexample_app_window_class_init (ExampleAppWindowClass *class){}ExampleAppWindow *example_app_window_new (ExampleApp *app){return g_object_new (EXAMPLE_APP_WINDOW_TYPE, "application", app, NULL);}voidexample_app_window_open (ExampleAppWindow *win,GFile *file){}
作为我们应用程序初始化中的一部分,我们创建一个图标和一个桌面文件。

[Desktop Entry]Type=ApplicationName=ExampleIcon=exampleappStartupNotify=trueExec=@bindir@/exampleapp
注意 @bindir@需要被实际的二进制文件路径替代,这样桌面文件才能使用。
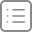
这就是目前我们实现的:

至今我们的程序并没那么瞩目,但是它已经在会话总线上出现,它有单个实例,而且它接受文件作为命令行参数。